S8050 NPN Transistor
- Low Voltage, High Current NPN Transistor
- Small Signal Transistor
- Maximum Power: 2 Watts
- Maximum DC Current Gain (hFE) is 400
- Continuous Collector current (IC) is 700mA
- Base- Emitter Voltage (VBE) is 5V
- Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCE) is 20V
- Collector-Base Voltage (VCB) is 30V
- High Used in push-pull configuration doe Class B amplifiers
In stock
₨ 5
In stock
Brief Description on S8050
S8050 is a NPN transistor hence the collector and emitter will be left open (Reverse biased) when the base pin is held at ground and will be closed (Forward biased) when a signal is provided to base pin. It has a maximum gain value of 400; this value determines the amplification capacity of the transistor normally S8050. Since it is very high it is normally used for amplification purposes. However at a normal operating collector current the typical value of gain will be 110. The maximum amount of current that could flow through the Collector pin is 700mA, hence we cannot drive loads that consume more than 700mA using this transistor. To bias a transistor we have to supply current to base pin, this current (IB) should be limited to 5mA.
When this transistor is fully biased then it can allow a maximum of 700mA to flow across the collector and emitter. This stage is called Saturation Region and the typical voltage allowed across the Collector-Emitter (VCE) or Collector-Base (VCB) could be 20V and 30V respectively. When base current is removed the transistor becomes fully off, this stage is called as the Cut-off Region.
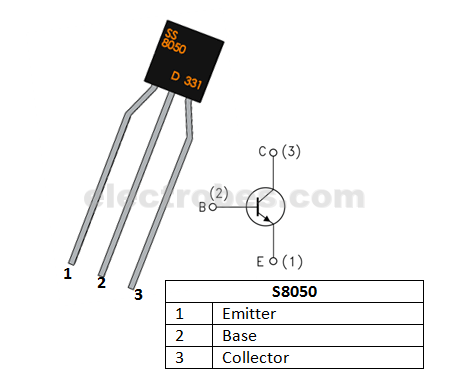
S8050 Pin Description
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
| 1 | Emitter | Current Drains out through emitter |
| 2 | Base | Controls the biasing of transistor |
| 3 | Collector | Current flows in through collector |
S8050 in Push-Pull Configuration
As mentioned in the features the S8050 transistor is commonly used in push pull configuration with Class B amplifier. So let us discuss how that is done.
A push pull amplifier, commonly known as Class B amplifier is type of multistage amplifier commonly used for audio amplification of loudspeakers. It is very simple to construct and requires two identical complimentary transistors operate. By complimentary it means that we need a NPN transistor and its equivalent PNP transistor. Like here the NPN transistor will be S8050 and its equivalent PNP transistor will be S8550. A simple circuit diagram of the Class B amplifier with the using the S8050 is shown below.
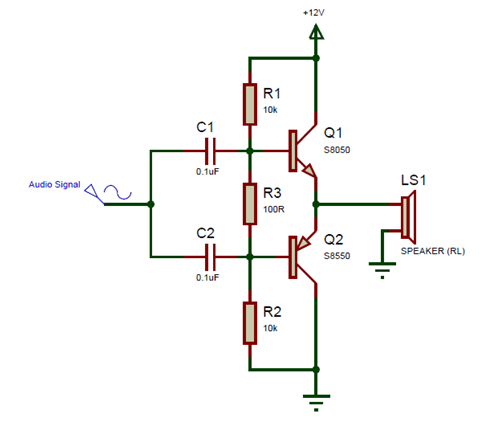
Applications
- Audio Amplification Circuits
- Class B Amplifiers
- Push pull Transistors
- Circuits where high gain is required
- Low signal applications
Based on 0 reviews
Be the first to review “S8050 NPN Transistor”
You must be logged in to post a review.










There are no reviews yet.